CHHANW: Economic and Health Impact Assessment of Heat Adaptation Action: Case Studies from India
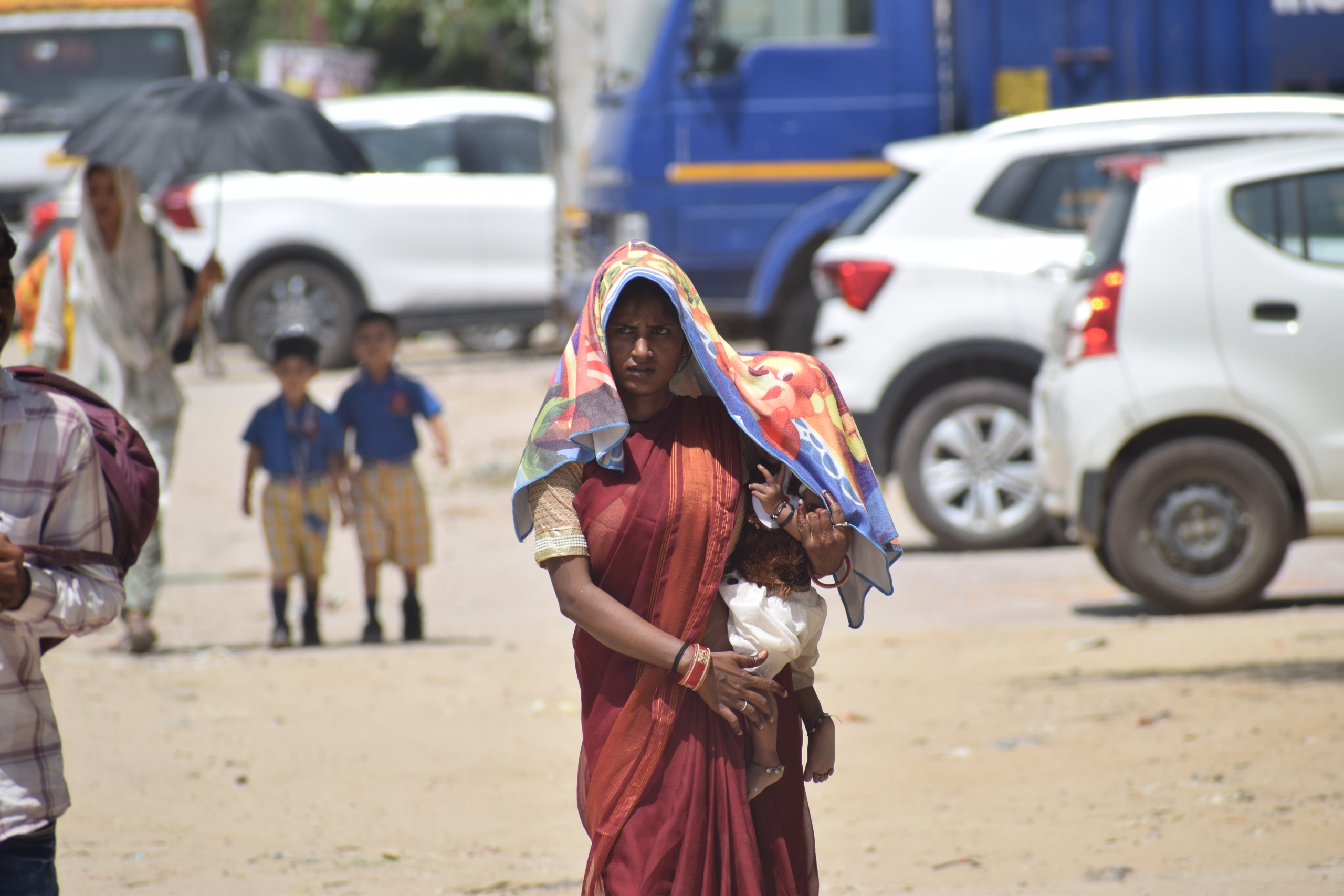

Credit: Sudarshan Jha / Shutterstock
Partners






Overview
Economic and Health Impact Assessment of Heat Adaptation Actions: Case Studies from India
Key Facts
The Health-Climate Link
Rising temperatures and recurring heatwaves pose severe risks to health, especially for vulnerable groups such as children, the elderly, and outdoor workers in India. These conditions exacerbate illnesses like dehydration, heatstroke, and respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Effective adaptation strategies are critical to safeguarding public health and mitigating socio-economic impacts.
The Project Advantage
Led by the Institute of Economic Growth, this study evaluates existing Heat Action Plans (HAPs) and pilots new household-level interventions across Bhubaneswar (Odisha) and Jaipur (Rajasthan). By combining health, economic, and environmental assessments, the project aims to deliver evidence-based recommendations for scalable and cost-effective heat adaptation strategies.
Key Interventions Include:
- Testing adaptation kits for households, including water bottles, Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS) packets, and heat protective gear.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of public health communication through apps and media campaigns.
- Simulating urban-scale interventions like cooling measures to inform policy design.
Aims and Objectives
This project aims to reduce heat-related health risks and quantify the economic impacts of heat adaptation measures in urban India.
Objectives of this study:
- Assess the effectiveness of current Heat Action Plans in protecting vulnerable populations.
- Pilot and evaluate additional heat adaptation interventions tailored to local contexts.
- Quantify the economic value of avoided health risks and associated costs.
- Provide data-driven recommendations to strengthen urban heat management policies.
Study design and methods
Study Design
Overview
This project evaluates the effectiveness of Heat Action Plans (HAPs) and pilots new heat adaptation strategies in Bhubaneswar (Odisha), Jodhpur and Jaipur (Rajasthan), heat-prone cities in India. The study integrates economic, health, and environmental assessments to identify cost-effective, scalable solutions that address urban heat risks while protecting vulnerable populations.
Interventions
- Adaptation Kits: Testing household kits, including items like oral rehydration salts (ORS), water bottles, and heat-protective gear.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Leveraging apps, local media, and public service messages to educate communities about heat risks and protection measures.
- Policy and Urban-Scale Strategies: Simulating urban cooling measures and strengthening Heat Action Plans through localized data and evidence.
Activities
Qualitative Research
Conducting interviews and focus groups with stakeholders, including local government officials, health workers, and community members, to understand perceptions and needs related to heat adaptation.
Intervention Pilots
Testing the effectiveness of adaptation kits and public awareness strategies in select households across Bhubaneswar (Odisha), Jodhpur and Jaipur (Rajasthan).
Economic Analysis
Quantifying the cost-benefit ratio of avoided heat-related illnesses to assess the economic value of implemented interventions.
Policy Integration
Using study findings to refine and strengthen Heat Action Plans, ensuring that they are inclusive, data-driven, and responsive to local needs.
Methods
Tracked Outcomes
- Health: Reducing heat-related illnesses and mortality.
- Economic: Estimating cost savings from avoided health impacts and improved productivity.
- Behavioural: Measuring community awareness and behaviour changes following intervention implementation.
Novel Methodology
Integrating health and economic impact assessments to evaluate adaptation strategies. The study uses a mix of qualitative data collection, economic modelling, and community co-design to ensure culturally appropriate, actionable outcomes.